What is Event Delegation?
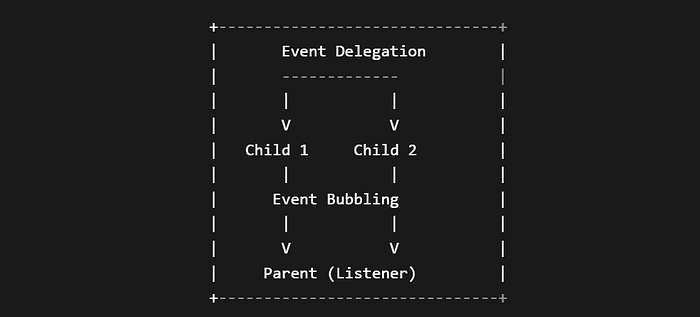
Event delegation is a technique that involves leveraging event bubbling to manage events at a higher level in the DOM rather than attaching event listeners to each element. This is particularly useful when you have many elements or when elements are dynamically added or removed.
What is Event Bubbling?
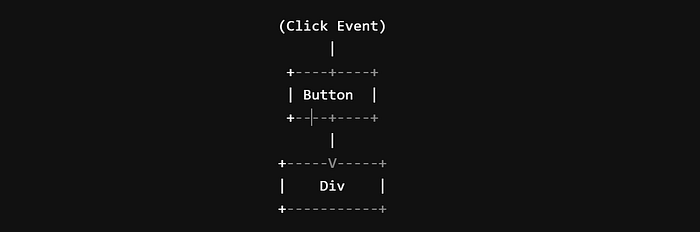
Before diving into event delegation, it’s crucial to understand event bubbling. When an event occurs on an element, it first triggers the target element and then bubbles up to its ancestors. For example, if you click on a button inside a div, the click event will first be fired on the button and then on the div.
To visualize this, imagine jumping into a swimming pool from a height of 20 feet. When your head touches the water (like clicking the button), your whole body follows and sinks (like the event bubbling up to the div).
How Event Delegation Works
Instead of attaching event listeners to each child element, you attach a single listener to the parent. This listener can then manage events for all its children, taking advantage of event bubbling. Here’s a basic example:
<ul id=”parent”>
<li>Item 1</li>
<li>Item 2</li>
<li>Item 3</li>
</ul>
<script>
document.getElementById('parent').addEventListener('click', function(event) {
if (event.target.tagName === 'LI') {
console.log('Clicked on:', event.target.textContent);
}
});
</script>
In this example, instead of adding a click event listener to each <li>, a single listener is added to the <ul>, which handles clicks on any of its child <li> elements.
Benefits of Event Delegation
Improved Performance
Attaching event listeners to many elements can lead to significant performance overhead, especially if the elements are frequently added or removed. Event delegation reduces the number of event listeners, leading to better performance.
For instance, imagine you’re making an interactive piano web application. Instead of using events for every key click, you can delegate the event to the parent. This way, a single listener will handle the whole event mechanism, making it much more efficient.
Simplified Code
Managing events through delegation can simplify your code, making it easier to read and maintain. Instead of scattering event listeners throughout your codebase, you can handle events in centralized logic.
Dynamically Added Elements
Event delegation is beneficial for dynamically added elements. If you add elements after the initial load, you don’t need to worry about attaching event listeners to them individually. The delegated event listener will handle them automatically.
Practical Use Cases for Event Delegation
Handling User Interactions in Dynamic Lists
Here’s an example of managing a dynamic list with event delegation:
<ul id=”dynamic-list”>
<li>Initial Item</li>
</ul>
<button id=”add-item”>Add Item</button>
<script>
const list = document.getElementById('dynamic-list');
const addItemButton = document.getElementById('add-item');
list.addEventListener('click', function(event) {
if (event.target.tagName === 'LI') {
event.target.remove();
}
});
addItemButton.addEventListener('click', function() {
const newItem = document.createElement('li');
newItem.textContent = 'New Item';
list.appendChild(newItem);
});
</script>
In this example, clicking on any list item removes it, and new items can be added dynamically without needing additional event listeners.
Managing Form Inputs
Forms with multiple inputs can benefit from event delegation:
<form id=”user-form”>
<input type=”text” name=”firstName” placeholder=”First Name”>
<input type=”text” name=”lastName” placeholder=”Last Name”>
<input type=”email” name=”email” placeholder=”Email”>
</form>
<script>
document.getElementById('user-form').addEventListener('input', function(event) {
if (event.target.tagName === 'INPUT') {
console.log(`${event.target.name}: ${event.target.value}`);
}
});
</script>
Here, any input change within the form is logged, simplifying the management of input events.
Tips for Effective Event Delegation
1. Use Appropriate Event Types: Choose the right event types for delegation. Click events are common, but other types like input, change, and keydown can also be effectively delegated.
2.Optimize Event Handlers: Ensure your event handlers are efficient to avoid performance issues.
3. Use Event Properties: Leverage properties like event.target and event.currentTarget to accurately determine the event source and context.
4. Consider Specificity: Be mindful of event specificity. Use specific selectors and conditions to filter events accurately.
Resources
For further reading on event delegation and related concepts, check out these resources:
2. Event Delegation by JavaScript.info
3. Event Delegation by David Walsh
Conclusion
Event delegation is a powerful technique that can significantly improve the performance and maintainability of your JavaScript code. By leveraging event bubbling, you can manage events efficiently, especially in dynamic and large-scale applications. Next time you find yourself adding multiple event listeners, consider using event delegation to simplify your code and enhance its performance. Happy coding! 💻