What is Selenium?
Selenium is an open-source, automated testing tool used to test web applications across multiple browsers. It’s primarily built in Java and supports several browsers and programming languages.
The Selenium test suite comprises of four tools:
- Selenium Integrated Development Environment (IDE)
- Selenium Remote Control (RC)
- Selenium WebDriver
- Selenium Grid
Need for Selenium WebDriver
To understand why WebDriver was introduced, let’s look at the shortcomings of Selenium RC.
Selenium Remote Control (RC) is a test tool that allows you to write automated web application UI tests in any programming language against any HTTP website using any mainstream JavaScript-enabled browser.

Selenium RC Server receives Selenium commands from your test program, interprets them, and reports the results back to the program.
The Web browser is injected with Selenium core, which interprets and executes the Selenese commands used in the test script.
The web browser now interacts with the webserver accordingly. This setup, however, complicates the architecture and takes additional time for execution.
What is Selenium WebDriver?
Paul Hammant developed Selenium WebDriver in 2006. Selenium WebDriver was the first cross-platform testing framework that could configure and control the browsers on the OS level.
It served as a programming interface to create and run test cases.
WebDriver performs actions on web elements. It supports various programming languages like Java, C#, PHP, and Python, among others.
It can also be integrated with frameworks like TestNG and JUnit for test management.
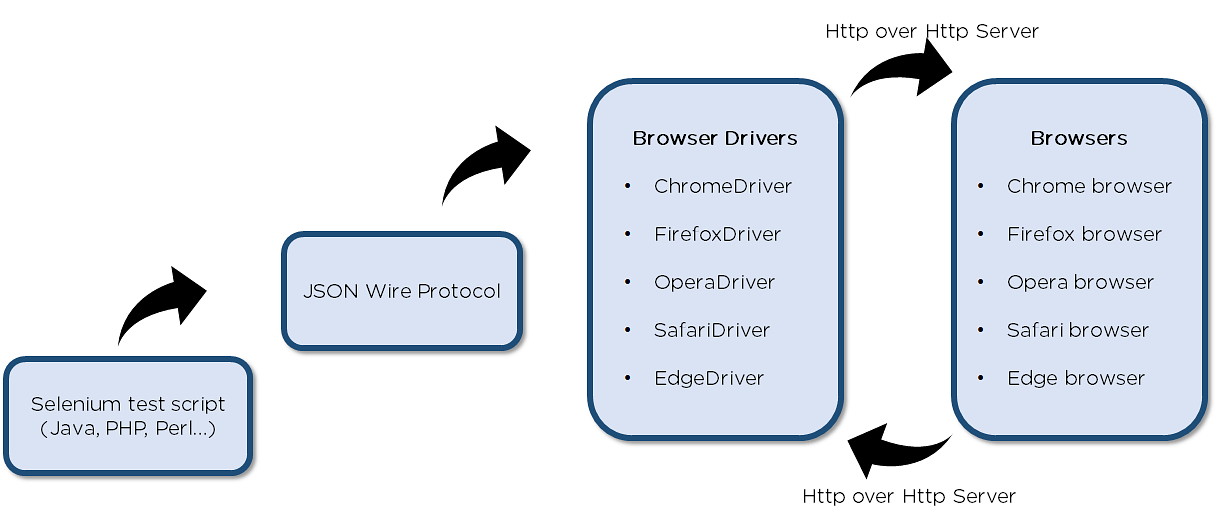
- Selenium test script – Selenium test script is the test code written in any of the mentioned programming languages that are interpreted by the driver
- JSON Wire Protocol – JSON Wire Protocol provides a transport mechanism to transfer data between a server and a client. JSON Wire Protocol is the industry standard for various web services
- Browser drivers – Selenium uses drivers, specific to each browser to establish a secure connection with the browser
- Browsers – Selenium WebDriver supports multiple web browsers to test and run applications on
What is XPath?
XPath is a Selenium technique that is used to navigate through the HTML structure of a webpage.
It is a syntax or language that makes finding elements on a webpage possible using XML path expression.
In Selenium automation, there may be times when elements cannot be found with general locators like ID, name, class, etc. And this is when XPath is used to locate those elements on the webpage.
XPath in Selenium may be used on both XML and HTML documents
Syntax of XPath :
XPath in Selenium provides many essential XPath functions and axes to write effective XPaths of the web elements and define unique locators.
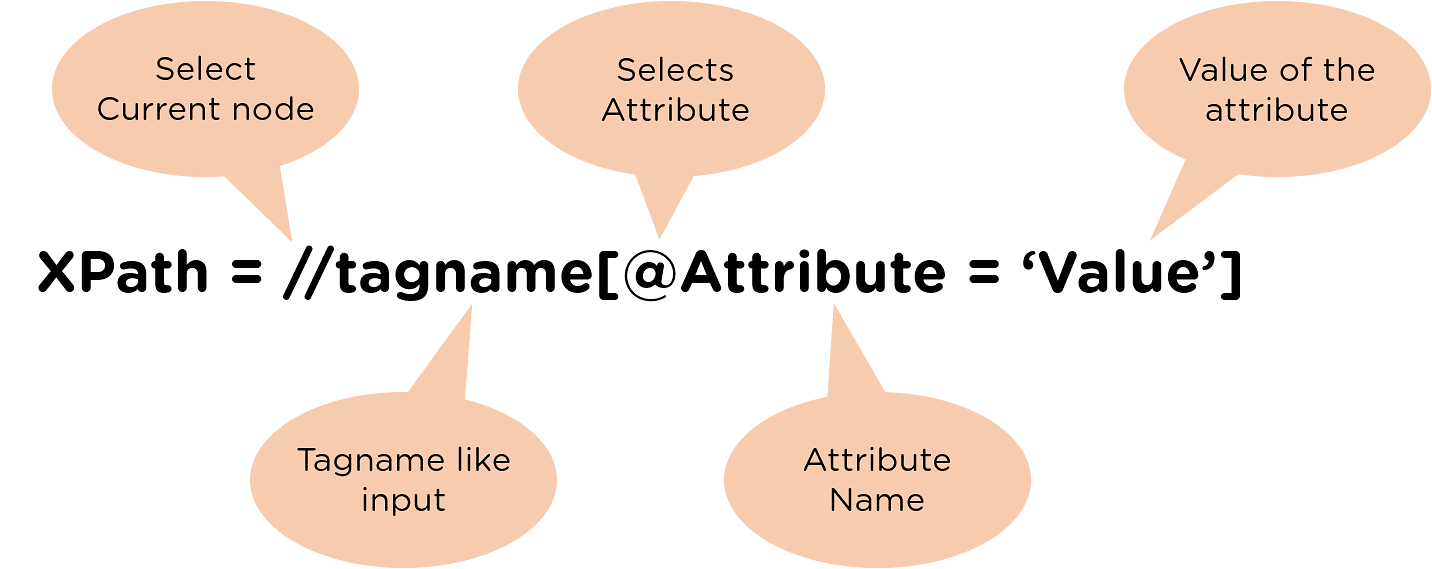
- // : to select the current node.
- tag name: tag name of a specific node.
- @: to select the attribute.
- attribute: it is the attribute name of the node.
- value: it is the value of the node.
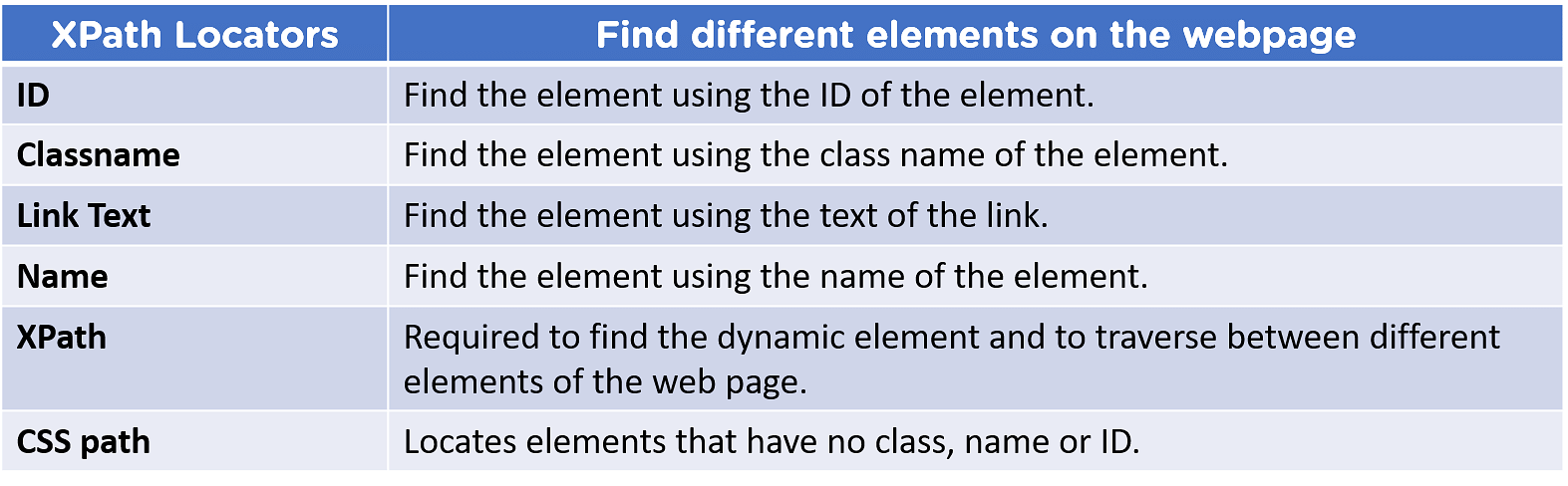
Types of XPath Locators :
There are several types of locators to find the element on web pages accurately.
Types of XPath
There are two different types of XPath:
- Absolute XPath
- Relative XPath
Absolute XPath
Absolute XPath refers to the direct way of finding an element. The major drawback of Absolute XPath is that if there are any changes in the element’s path, then the XPath will fail.
The XPath begins with a single forward-slash (/), which states that the element can be selected from the root node.
The syntax of the Absolute XPath looks like this:
| Absolute XPath:/html/body/div[1]/div/div[2]/header/div/div[2]/a/img |
Relative XPath
In the case of Relative XPath, the path begins from the middle of the HTML DOM structure. Here, the structure starts with a double forward-slash (//) that states that the element can be searched anywhere on the webpage.
Relative XPath enables you to write from the middle of the HTML DOM structure without any need to write a long XPath.
The syntax of the Relative XPath looks like this:
| Relative XPath://*[@id=”block-perfecto-main-menu”]/ul/li[6]/a |